 Glen Vary’s co-defendant Frederick Relerford swears accomplice was Julius McElroy, not Vary
Glen Vary’s co-defendant Frederick Relerford swears accomplice was Julius McElroy, not Vary
Flint police found gun used to kill victim Robert Montgomery in McElroy’s pocket after he was killed by his girl friend

Ricardo Ferrell
Flint police misconduct? Flint Police Sgt. Shawn Ellis prompted 2 other witnesses to ID Vary, known as ‘Bay Bay’ based on third party hearsay
Witness later met Vary, said he “knew that the wrong person had been locked up for shooting DJ.”
Jury ignored alibi witnesses; study says this happens more frequently in cases of Black defendants
By Ricardo Ferrell, VOD Field Editor
With Diane Bukowski, VOD Editor

Glen Vary (MDOC photo)
DETROIT — Flint native Glen Vary, now 37, has been serving a life without parole sentence for 17 years since his conviction for the 2003 murder of Robert “DJ” Montgomery and the wounding of Darwin McMullen outside a house in Flint.
Vary’s co-defendant Frederick Relerford, and three other witnesses have testified or executed sworn affidavits over the years stating that he was definitely not involved in the Montgomery killing.
During Vary’s trial, victim McMullen testified that his identification of Vary in a photo line-up was prompted by Flint Police Sgt. Shawn Ellis, the officer in charge of the case. He said Ellis told him that a third party known only as “Alex” told police Vary was involved.
Witness Cawon Lyles said Ellis similarly told him Vary (known as ‘Bay Bay’) was the killer. But after later meeting Vary at the prison where both were incarcerated, he said it was definitely not him.

Judge F. Kay Behm
After Vary’s second motion for relief from judgment, Genesee County Circuit Court trial Judith Anne Fullerton set an evidentiary hearing for Dec. 17, 2017 to hear testimony from witness Cowan Lyles and others corroborating his claim of innocence.
But that hearing has been postponed over and over again, first pending a hearing on federal charges against Lyles, then due to the transfer of his case to a second and then a third judge, as well as scheduling conflicts. No new date for a hearing in front of Genesee County Circuit Court Judge F. Kay Behm has yet been set.

Vary’s case was sent to Michigan Attorney General Dana Nessel’s Conviction Integrity Unit, but Vary says they told him to wait until after the long-delayed evidentiary hearing is held. The AG’s press representative told VOD, “We can confirm that we received an application, but cannot comment on an open file. It should be noted that Mr. Vary has counsel.”

Atty. Phillip Comorski with client Michael Powels during 2019 court hearing where Powels was exonerated.
VOD called Vary’s attorney Phillip Comorski, but had not heard back from him by press time.
Comorski emphatically presented his client’s case in a federal habeas proceeding in 2010, saying that there was no real evidence at trial implicating Vary.
“The victim who survived the shooting (the driver, Darwin McMullen) testified that when he spoke to Sgt. Ellis during the ongoing investigation, he informed him that he “heard” from other third parties (namely an individual named Alex) that Petitioner was one of the persons involved in the incident (T, Vol II, pp 108-111; 119; 143-144). It was then that he was able to “identify” Petitioner from a photograph, because he did not even know Petitioner or the other defendant, and was supplied the information concerning their complicity from third parties (T, Vol II, pp 143-145). This is hardly identification testimony that is “merely flawed”; rather, the evidence presented at trial clearly demonstrates that the identification of Petitioner (the only real evidence that implicated him in the crime) was generated by hearsay and rumor information supplied by third parties.” See http://voiceofdetroit.net/wp-content/uploads/Glen-VARY_REPLY-TO-AUSA-RESPONSE-6-4-10-2.pdf.

Exonerees Justly Johnson (l) and Kendrick Scott (r) with PI Scott Lewis at Proving Innocence conference in 2019.
Private Investigator and former TV news reporter Scott Lewis was hired in 2014 to investigate Vary’s case and has done extensive work on it. Lewis told VOD, “I don’t know why this case is still languishing in court. It sure does seem like a pretty strong case of actual innocence.”
Lewis took a sworn affidavit from Vary’s co-defendant, Frederick Relerford, who is also serving life without parole, in 2019. Relerford said his accomplice at the crime scene was Julius McElroy, now deceased. He said Vary had nothing to do with the crime and that he didn’t even know him then.
Previously, Vary said in his motion for habeas relief, he had planned to have Relerford testify at his sentencing hearing in 2004, but Relerford was not called to do so. In his 2010 brief, Comorski attributed that to the “ineffective assistance” of Vary’s trial counsel.

http://voiceofdetroit.net/wp-content/uploads/Frederick-Relerford-Affidavit-2.pdf
In his report, Lewis said, “The investigator learned through court records that a man named Julius McElroy, who was shot and killed by his girlfriend in Flint in 2004, had the murder weapon from the Glen Vary case in his pocket when authorities arrived at the scene. Also, in a court proceeding, McElroy’s girlfriend, Nikki Minor, testified that McElroy had this weapon in his possession from November of 2002, before the murder.”

Julius McElroy in Flint PD photo obtained by Scott Lewis.
In his affidavit, Relerford explained that he and McElroy were first approached by a man looking to buy marijuana on Dec. 18, 2003, but McElroy pulled out a gun after the potential customer pulled out “a few dollars,” robbed the man and took his phone. He says they walked away to Mt. Elliott Street, and that McElroy approached a car with two men in it and decided to take the car, telling Relerford to drive it. (See link to full affidavit above.)
“McElroy came around to the driver’s side to help,” Relerford said. “That’s when I heard three shots go off . . McElroy went up to the car and it looked like he was about to pull the dead guy out of the car. I said, ‘I’m out of this bitch,’ and took off running. McElroy started running too and we ran all the way to our homeboy’s house.”
 Feronda Smith – National Registry of Exonerations (umich.edu)
Feronda Smith – National Registry of Exonerations (umich.edu)
In his 2014 interview with P.I. Lewis, Cawon Lyles said that Flint police [Sgt. Ellis, the chief investigator] told him that one of the gunmen who robbed him just before the murder of Robert Montgomery was Vary, known as “Bay Bay.” He told Lewis that he knew “DJ,” the murder victim, from the neighborhood. He said he went to buy marijuana from him, but was robbed near DJ’s house just before the murder.

Gus Harrison CF in Ionia, MI
Lewis wrote further. “Lyles stated that he first met Bay Bay through a chance encounter after he was incarcerated at the Gus Harrison Correctional Facility in Adrian. . . . Lyles stated that as he was walking toward the gym he saw three guys walking and one was a familiar face.
“He said that he asked who was from Flint and one of the men said, “we all from Flint.” Lyles stated that he asked the guy from Flint if Bay Bay was there because he wanted to confront him about robbing him years earlier. He stated that one of the men said, “I am Bay Bay and I never robbed you.” Lyles said he then asked if there was another person in from Flint named Bay Bay in level 2, and Bay Bay stated, “No, I’m the only one.”
Lyles said he then asked Bay Bay what he was locked up for and Bay Bay stated, “for something I didn’t do.” Lyles stated he then asked Bay Bay if he was locked up for shooting DJ and he replied, “yes.” Lyles stated that’s when he knew that the wrong person had been locked up for shooting DJ because Bay Bay was not one of the men who robbed him and then walked down Mt. Elliott toward the area where DJ was.
Lewis said he then conducted a “blind sequential photo array” of 11 photos which he showed Lyles one at a time, with the proviso that the man who robbed him was not necessarily in the photos.
“Approximately three or four photos into the array, Mr. Lyles asked the investigator to put a picture face down on the table and let him view the rest of the photos. Upon completion of viewing all eleven photos, Lyles pointed to the picture lying face down on the table and stated, “that’s the man who robbed me.” The investigator then turned the photograph over and marked it with an X. The photo chosen by Lyles was the mug shot of Julius McElroy that the investigator obtained from the Flint Police Department.

Prof. Colin Miller, Univ. of South Carolina School of Law
Two alibi witnesses, Vary’s former girl friend and her mother, testified at trial that Vary was with them the entire day of the murder, celebrating the holiday season. Vary’s trial jury evidently did not believe them.
Professor Colin Miller is with the University of South Carolina School of Law. The ABA Journal named him of their top WEB 100 in 2017, citing his podcasts “Evidence Prof,” and “Undisclosed.”
In an Undisclosed podcast on the case of Darrell Ewing, extensively covered by VOD, he observed, “As we see all too often, in the American criminal justice system, jurors tend to reject alibis by African American witnesses, even if there is no evidence refuting their recollections. Perhaps the most infamous case in this vein is the case made famous by Bryan Stevenson in his book “Just Mercy” and the ensuing film: the case of Walter McMillian.”

In the movie “Just Mercy” a witness recantation saved defendant Walter McMillian from execution, exonerated him.
Ricardo Ferrell: In the meantime Vary remains locked up for a crime that evidence shows he’s innocent of, and the longer his case is delayed, the longer he’ll be in prison. We have a justice system that supposed to be fair to all under the law, but in the Vary case there’s a grave travesty of justice.
When Gilbert Poole was exonerated in May, Attorney General Dana Nessel was quoted saying, “This serves as an example of the important work being done by our CIU,” Nessel said. This is another case where such work needs to be done and should be immediately reviewed by the Statewide Conviction Integrity Unit, in order to exonerate Glen Vary for an obvious wrongful conviction.
**********************************************************************************

 Voice of Detroit is a pro bono newspaper, now devoting itself entirely to stories related to our PRISON NATION and POLICE STATE.
Voice of Detroit is a pro bono newspaper, now devoting itself entirely to stories related to our PRISON NATION and POLICE STATE.
VOD’s editors and reporters, most of whom live on fixed incomes or are incarcerated, are not paid for their work. Ongoing costs include quarterly web charges of $435,00, P.O. box fee of $180/yr. and costs for research including court records and internet fees, office supplies, gas, etc.
Please DONATE TO VOD at:
**********************************************************************************




 Voice of Detroit sincerely thanks all who contributed to keep VOD on-line in the last 2 weeks! We have paid the quarterly webhosting fee of $435 as a result and are making renewed headway on other bills.
Voice of Detroit sincerely thanks all who contributed to keep VOD on-line in the last 2 weeks! We have paid the quarterly webhosting fee of $435 as a result and are making renewed headway on other bills.






 Our Demands Are Such:
Our Demands Are Such: Apply the New York State minimum wage law to all state institutions. STOP SLAVE LABOR.
Apply the New York State minimum wage law to all state institutions. STOP SLAVE LABOR. Educate all correctional officers to the needs of the inmates, i.e., understanding rather than punishment.
Educate all correctional officers to the needs of the inmates, i.e., understanding rather than punishment. We, the men of Attica Prison, have been committed to the New York State Department of Corrections by the people of society for the purpose of correcting what has been deemed as social errors in behavior. Errors which have classified us as socially unacceptable until reprogrammed with new values and more thorough understanding as to our values and responsibilities as members of the outside community. The Attica Prison program in its structure and conditions have been enslaved on the pages of this Manifesto of Demands with the blood, sweat, and tears of the inmates of this prison.
We, the men of Attica Prison, have been committed to the New York State Department of Corrections by the people of society for the purpose of correcting what has been deemed as social errors in behavior. Errors which have classified us as socially unacceptable until reprogrammed with new values and more thorough understanding as to our values and responsibilities as members of the outside community. The Attica Prison program in its structure and conditions have been enslaved on the pages of this Manifesto of Demands with the blood, sweat, and tears of the inmates of this prison. We Demand the constitutional rights of legal representation at the time of all parole board hearings and the protection from the procedures of the parole authorities whereby they permit no procedural safeguards such as an attorney for cross-examination of witnesses, witnesses in behalf of the parolee, at parole revocation hearings.
We Demand the constitutional rights of legal representation at the time of all parole board hearings and the protection from the procedures of the parole authorities whereby they permit no procedural safeguards such as an attorney for cross-examination of witnesses, witnesses in behalf of the parolee, at parole revocation hearings.

 We Demand that all prisoners be present at the time their cells and property are being searched by the correctional officers of state prisons.
We Demand that all prisoners be present at the time their cells and property are being searched by the correctional officers of state prisons.


 APPEAL to families and friends of prisoners, especially those whose cases we are covering–please chip in–any amount is appreciated!
APPEAL to families and friends of prisoners, especially those whose cases we are covering–please chip in–any amount is appreciated! SEPTEMBER 7, 2021
SEPTEMBER 7, 2021 Most stories are about prisoners from Detroit and Michigan who were wrongly convicted, sentenced as juveniles, or serving lengthy and natural life terms in the only country in the world that actually sends people to die in prison. Since the historic June 4 rally against wrongful convictions outside Frank Murphy Hall, many families have been contacting VOD seeking stories about their loved ones inside the walls. We are keeping a list of stories to be done in the near future, and are committed to following up.
Most stories are about prisoners from Detroit and Michigan who were wrongly convicted, sentenced as juveniles, or serving lengthy and natural life terms in the only country in the world that actually sends people to die in prison. Since the historic June 4 rally against wrongful convictions outside Frank Murphy Hall, many families have been contacting VOD seeking stories about their loved ones inside the walls. We are keeping a list of stories to be done in the near future, and are committed to following up.










 Related:
Related:

 Glen Vary’s co-defendant Frederick Relerford swears accomplice was Julius McElroy, not Vary
Glen Vary’s co-defendant Frederick Relerford swears accomplice was Julius McElroy, not Vary














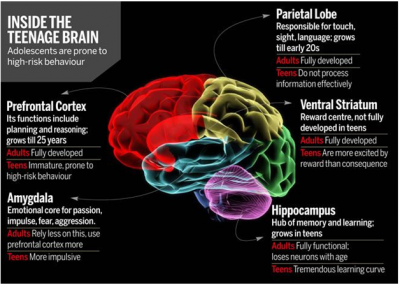 ”In light of the change in the law by the highest court in the land, and brain science research, how can we reasonably continue to allow the law to enhance the punishment of any person for a crime committed as an adolescent?” asks Shawanna Vaughn, Director of Silent Cry, Inc. who was recently appointed Ambassador of Reform Alliance Michigan. Reform Alliance was founded by rappers Meek Mill and Jay-Z to address reforms in parole and probation.
”In light of the change in the law by the highest court in the land, and brain science research, how can we reasonably continue to allow the law to enhance the punishment of any person for a crime committed as an adolescent?” asks Shawanna Vaughn, Director of Silent Cry, Inc. who was recently appointed Ambassador of Reform Alliance Michigan. Reform Alliance was founded by rappers Meek Mill and Jay-Z to address reforms in parole and probation.




 Once the disease begins proliferating inside prisons we are going to witness it produce potentially catastrophic results once again. While vaccination numbers may help curtail surges of hospitalizations and deaths, it won’t prevent people who have been vaccinated from the possibility of experiencing long-term symptoms.
Once the disease begins proliferating inside prisons we are going to witness it produce potentially catastrophic results once again. While vaccination numbers may help curtail surges of hospitalizations and deaths, it won’t prevent people who have been vaccinated from the possibility of experiencing long-term symptoms. Each time a person signs the petition an email is sent to their respective State Representative and State Senator calling on them to support passage of legislation reflecting the 10-Point Michigan Prison Reform Platform.
Each time a person signs the petition an email is sent to their respective State Representative and State Senator calling on them to support passage of legislation reflecting the 10-Point Michigan Prison Reform Platform.
 After postponing court hearings three times for Efrén Paredes, Jr since March 2021, Berrien County Trial Court Judge Charles LaSata has scheduled a court hearing in the case to be convened September 10, 2021.
After postponing court hearings three times for Efrén Paredes, Jr since March 2021, Berrien County Trial Court Judge Charles LaSata has scheduled a court hearing in the case to be convened September 10, 2021.




